What is SAP HANA? A Complete Overview for Beginners
The term is quite popular nowadays in the tech world. SAP HANA which is the abbreviation of High Performance, Analytic Appliance is a database whose primary function is to store and retrieve data as requested by applications from both SAP and non-SAP. Further for your knowledge or you probably already know about that.
It is developed and marketed by SAP and was introduced first time in 2010. So as compared to traditional databases;

what makes SAP HANA database special?
SAP HANA actually is more than just a database. We can also call it a platform which combines database, data processing and application perform capabilities
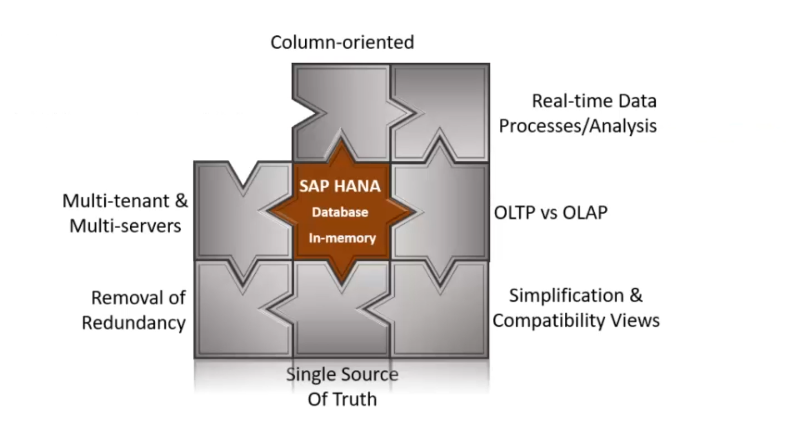
Characteristics of SAP HANA database:
A. In-Memory :
data is stored and processed in-memory,i.e., RAM and no longer on a hard drive. For example, in old computers you have noticed or even in recent computers as well that the data is stored in hard drive. but when you open an application, for example, a browser or any other application so temporarily it is stored into RAM so that you can access that faster because if you will open a new application, so you notice that it takes time to open it through the hard disk. But in RAM, if it is already open so it just clicks and opens it. So, that is the first characteristic of SAP HANA that the data is stored and processed in-memory. So, from here you can imagine how fast this database will be.
B. Column-Oriented:
It does not mean that SAP HANA is column-based database only, rather it connects both column-based and row-based database technology or in other words, it supports both row-store and column-store tables.
For your knowledge, row-based storage is suitable for write operations of data or to process only one record at a time.so that is transactional data.While column-based storage is suitable for read operations of data or to process large number of records such as calculations, scanning, aggregations etc.
So why specifically SAP HANA is called column-oriented? The reason is that high performance is achieved when column-store tables are used in-memory which shows that work loads on enterprise databases are mostly read-oriented.
So, row-based storage is for write operations and column-based storage is for read operations.
C. Real-time data processes or analysis:
Real time data processes or analysis is because the data is stored in-memory, it can be accessed real time. There is no delay.
In other words in-memory database technology allows the processing of massive amounts of real-time data in a short time. There is no delay.
Further, Real-time analysis and reporting are possible in embedded SAP Business Warehouse which is BW powered by HANA.
D. OLTP vs OLAP:
The next characteristic of SAP HANA as I mentioned lies in both OLTP and OLAP processing.
OLTP refers “Online Transaction Processing” while OLAP refers “Online Analytical Processing”. They were separated from each other in the traditional database design. In other words, a database model was either built for OLTP optimization or OLAP optimization, but not both.
Now SAP HANA database supports both OLTP and OLAP processing and we do not need to move transactional data to a separate system, as some organizations are still doing that. Because the advantage is, the same table runs both transactional and analytical applications, And so the data is available in real time at every level of detail.
as I mentioned previously Row storage table is good for transactional data. While column data storage is good for analytical data, so SAP HANA supports both row storage table and column storage table, the same table runs both transactional and analytical applications in SAP HANA database and we do not need to move transactional data to a separate system.
And the data is available in real time at every level of detail.
E. Simplification and Compatibility Views:
SAP HANA database simplifies the data model means that it consists only of the essentials tables which record business data and has expired index tables and aggregate tables.
In other words, there is no data redundancy, increase of transaction throughput and aggregations on the fly. And in the spirit of simplification, SAP HANA has introduced compatibility views.
F. Single source of truth:
The next characteristic, Single source of truth is one of the features of SAP HANA database. Based on a single source of truth, data is stored once in
the database table as compared to the traditional database where the data was repeated in different tables.
Any derived data can be calculated on the fly instead of being physically stored in the database. For example, 2 + 2 = 4
Now it doesn’t happen like 2 is stored in a different table + is stored in a different table, the second 2 is stored in another table and the result
is 4, stored in a different table.
it means that any derived data can be calculated on the fly instead of being physically stored in the database. So how we can get benefit out of this? It reduces the database size and additionally there is no duplication of data.
G. Removal of redundancy:
How SAP HANA removes redundancy?
First, before we discuss removal of redundancy, we need to understand why redundancy occurs?
It occurs when the data is repeated in different tables so SAP HANA database removes redundancy by expiring index tables and aggregate tables and has introduced compatibility views which do not need physical data in the expired tables.
As I just above gave you the example of 2 + 2 is equal to 4. So what happens, this leads to reduction of database footprint, increase of transaction throughput and aggregations on the fly.
H. Multi-tenant and Multi-servers:
The next characteristic is Multi-tenant and Multi-servers
What is Multi-tenant? Multi-tenant refers one instance of an application on a single HANA system shared by multiple customers or tenants but each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to other tenants.
for example you can take the example of a box which is shared by different companies and that box you can cut it into pieces, but each piece cannot be seen by people who actually own those pieces of box.
Similarly, SAP HANA database multi-tenant example is the same like in a house, there are different tenants are living.
Now, the question is how it is isolated? A single HANA system can be set up into multiple databases. In other words, a single container HANA system can be converted into multiple container databases HANA system.
As I just gave you the example of a house which is shared by different tenants. In SAP, the example can be SAP HANA Public Cloud.
The next point is multi-servers. So, SAP HANA has got multi-server approach. contains multiple servers such as Index Server, Name Server, Pre-processor Server, Statistics Server, and XS Server to process and execute logic for processing data.
I. Digital core:
SAP HANA supports digital core. It means that SAP HANA in-memory database allows organization to transform into digital business. You can access applications running on SAP HANA through cloud, mobile phone, tabs, iPad etc.
Now the question is, what is digital core?
Digital core actually includes next-generation technologies like Advanced analytics, Internet of things, Artificial intelligence and machine learning
that cannot be run on Legacy “I.T.” (infrastructure and traditional) database, so we can integrate and run all such technologies with SAP HANA database. you can see that a Digital core; how big benefit, it is to be used by SAP HANA.